IoT Certified OptoPartner shows us how to quickly retrofit a CNC mill with groov RIO
In a time when automation is driven by increasing connectivity, there is still plenty of everyday equipment that is simply not designed to talk to much of anything.
This equipment might be full of juicy data—how well it’s working, how much energy it’s using, how often it’s put to work—and leveraging that data to build an OEE or predictive maintenance program is often an untapped source of potential savings.
But what are your options for integrating this kind of equipment? Well, until recently they probably didn’t look very good.
- Maybe you could use a datalogger? Instrument the signals you are interested in, connect them to the logger, let it run for a week, then pull the data from it manually and make a big spreadsheet? Do that every week… Ugh. Nevermind.
- Invest in a more expensive continuous logger, RTU, or PLC? This can be a big investment for a single piece of equipment, and it doesn’t scale terribly well if you have multiple units.
- What about a Raspberry PI? Those things are great at connecting to stuff and they’re cheap. Except that they aren’t so great at working with industrial I/O signals and are maybe a little too fragile for a greasy machine shop or factory floor.
Been there? Us too. That’s why we created groov RIO to be connected, affordable, and rugged, with the software and processing power needed to simplify equipment retrofits like this.

Enginuity, an IoT Certified OptoPartner out of Nova Scotia, showed us how they tackled this problem on a CNC mill for which they wanted to collect historical data and develop a predictive maintenance plan.
With three measurements—vibration, temperature, and current—they could detect a variety of problems and indirectly measure power consumption, giving them a reliable reading of overall system health and usage.
But of course, the CNC didn’t provide any of these readings itself. So the first step was to instrument these signals directly.
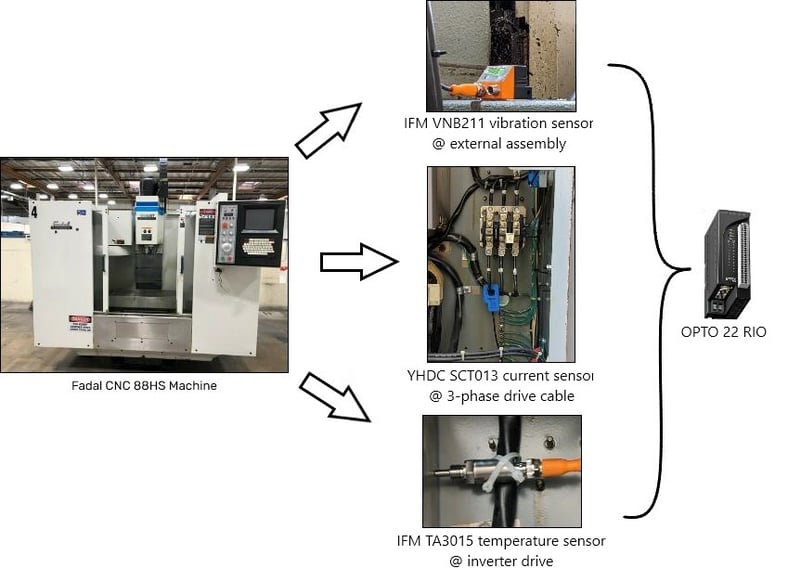
Enginuity connected signals of interest on the CNC to a groov RIO edge I/O module
After instrumenting the signals they wanted to collect, Enginuity connected the signal wires to a groov RIO edge I/O module. Using RIO’s embedded Node-RED IoT engine they created a real-time mobile dashboard and pushed data to OSI PI using REST calls.
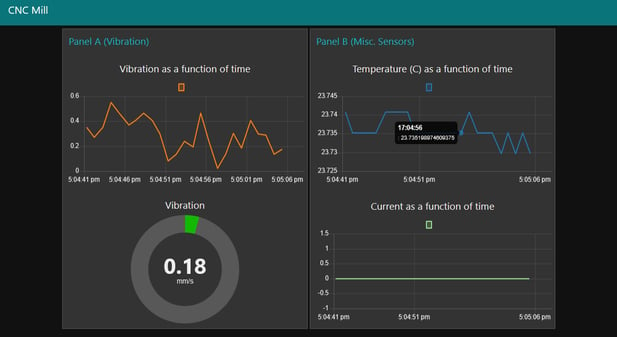
Node-RED dashboard view
They used the OSI PI system to generate email notifications based on sensor values and to connect data to Grafana for more detailed dashboard designs.
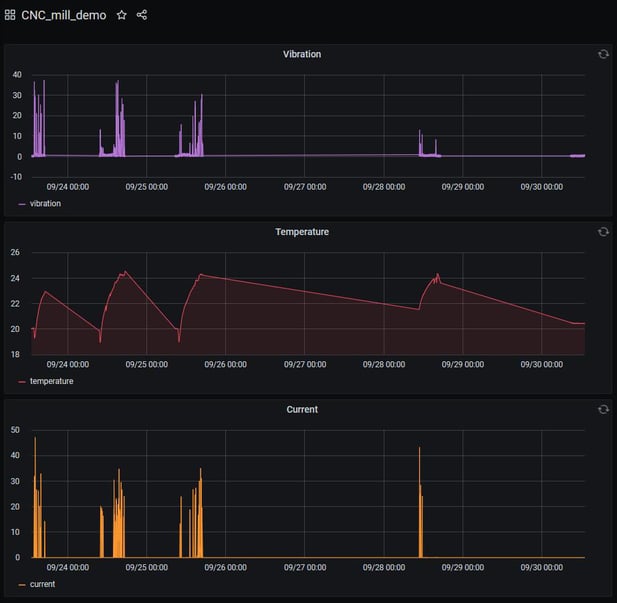
Grafana dashboard view showing 7-day trends of vibration, current, and temperature
Here's the data flow from end to end:
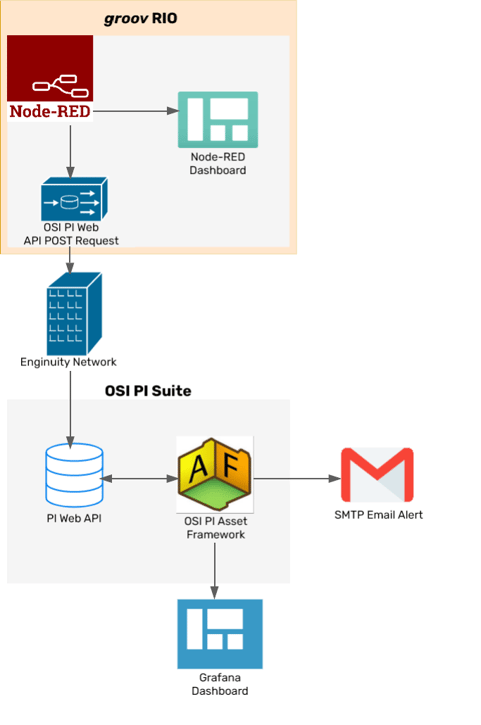
Flow of data from groov RIO to OSI PI system
Of course, Node-RED doesn't limit you to working with OSI PI. As an open platform, it's easy to build connections to dozens of different database systems, cloud services, and more.
Thanks to Enginuity for sharing their project with us. To learn more about their broad range of automation services, you can visit them at enginuityinc.ca or contact them at info@enginuityinc.ca or +1 (902) 431-7931.
We know there are many great groov RIO, groov EPIC and SNAP PAC projects happening every day. If you’d like to have yours featured here, please contact us or let us know in the comment section below.
