Loop the loop.
PID loops are used in a lot of different applications, and for good reason: they help keep our world under control. If you need to control a process temperature or pressure, you probably are going to use a PID loop. But are they always the right solution?
Ultra quick review; a proportional-integral-derivative control loop (or
PID controller) compares a setpoint against a measured input value, and depending on the error, changes a control variable (output). It’s all about math. A PID loop is all about running a mathematical formula over and over at a specific rate.
The most common example of a PID loop that I often talk about in our monthly training class is the cruise control on a car. The speed of the car is the input, the accelerator is the output and the setpoint is what speed the car is doing the moment the driver presses the “set” button.
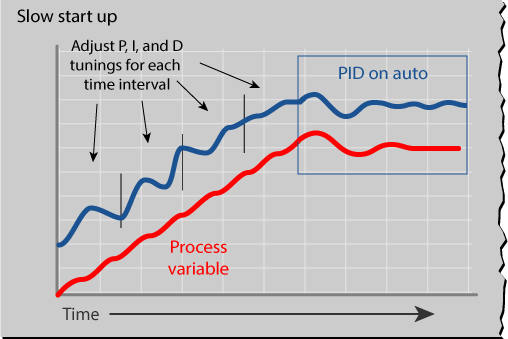
PID loops are so useful that sometimes we too quickly decide to use a one in a process when it may not be the best solution to the problem. In this week’s blog we are going to take a look at one instance where use of a PID loop may not be the best tool for the job.